Human Anatomy
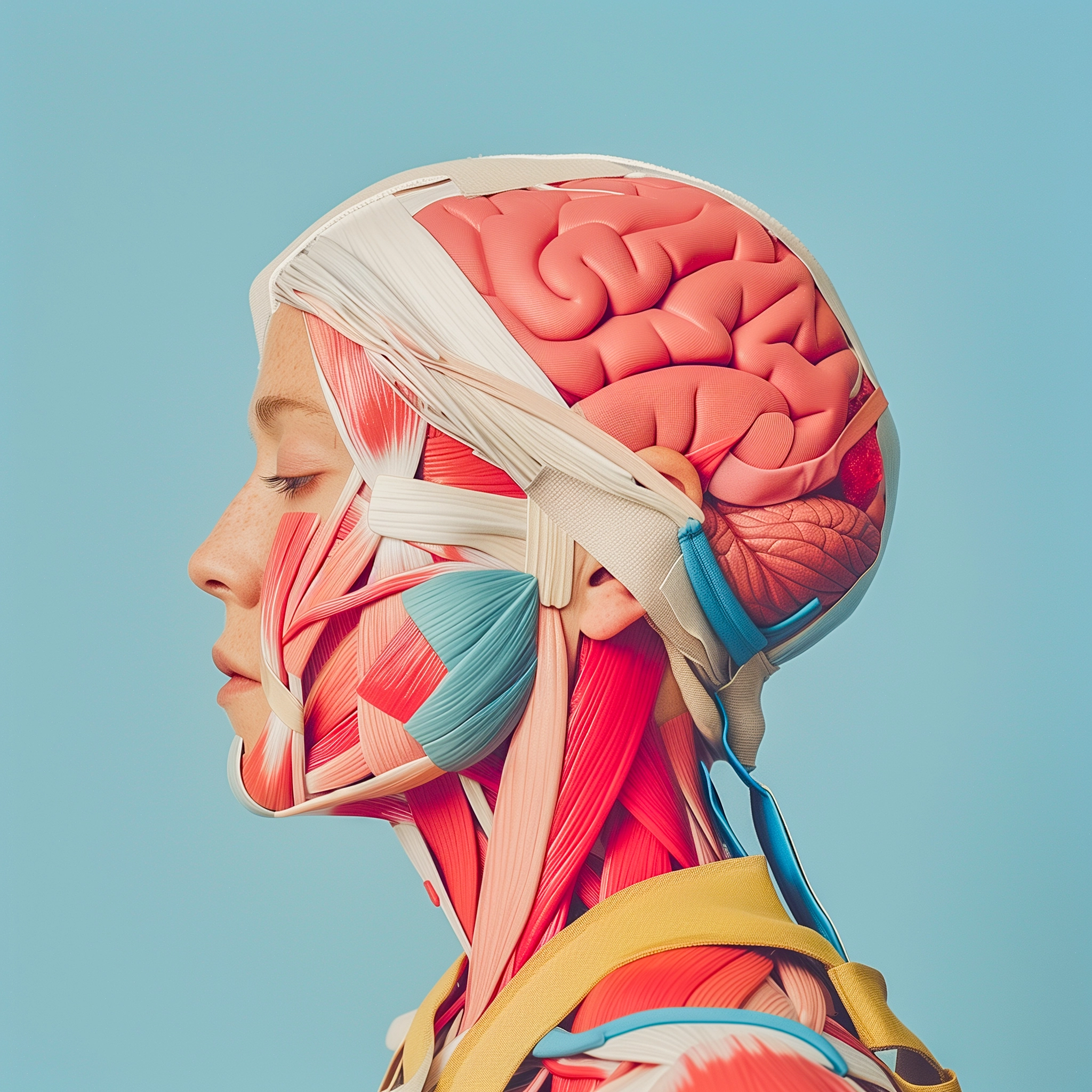
Brain
The complex organ that serves as the control center of the body, overseeing thoughts, movements, emotions, and sensory processing.
The brain is a highly specialized organ located within the skull, composed of billions of neurons and glial cells. It is responsible for processing sensory information, regulating bodily functions, and enabling cognition and memory. Encased in the protective structure of the cranium, the brain integrates signals from the body and environment, influencing behaviors and reactions.
Terminologia Anatomica
cerebrum
System
Nervous system
Function
The brain plays a vital role as the command center of the human body, coordinating both voluntary and involuntary actions. It processes sensory data from the environment through specialized regions like the occipital lobe for vision and the temporal lobe for hearing, enabling perception and interaction with the world. Beyond processing sensory input, the brain governs critical functions like breathing and heart rate regulation through the brainstem. Higher cognitive functions, such as thinking, reasoning, and planning, occur primarily in the cerebral cortex, where complex neural connections facilitate abstract thought and decision-making. The brain also plays a role in emotional regulation and memory formation, with specific regions such as the amygdala and hippocampus contributing to how emotions affect experiences and how memories are stored and recalled. Overall, the brain orchestrates the vast array of functions necessary for survival and adaptation to an ever-changing environment.
Location
Situated within the cranial cavity, the brain occupies the uppermost section of the central nervous system. It is divided into several distinct regions, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The cerebrum, the largest part, is located in the anterior and superior sections of the skull and is divided into left and right hemispheres, each responsible for different functions and controlling the opposite side of the body. Beneath the cerebrum lies the cerebellum, which is located at the back of the brain and plays a crucial role in coordination and balance. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and is critical for regulating automatic functions like breathing and heart rate. This precise location within the skull offers crucial protection from physical trauma, yet allows the brain to remain intricately connected to the body's intricate network of nerves.
Did You Know?
- The human brain contains about 86 billion neurons, each forming thousands of connections known as synapses.
- Despite weighing approximately 1.4 kilograms, the brain consumes about 20% of the body's total energy at rest.
- The brain generates enough energy to power a small light bulb when awake.
- Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to adapt and reorganize itself by forming new connections throughout life, allowing for learning and recovery from injury.
- The brain can produce approximately 100,000 chemical reactions every second.