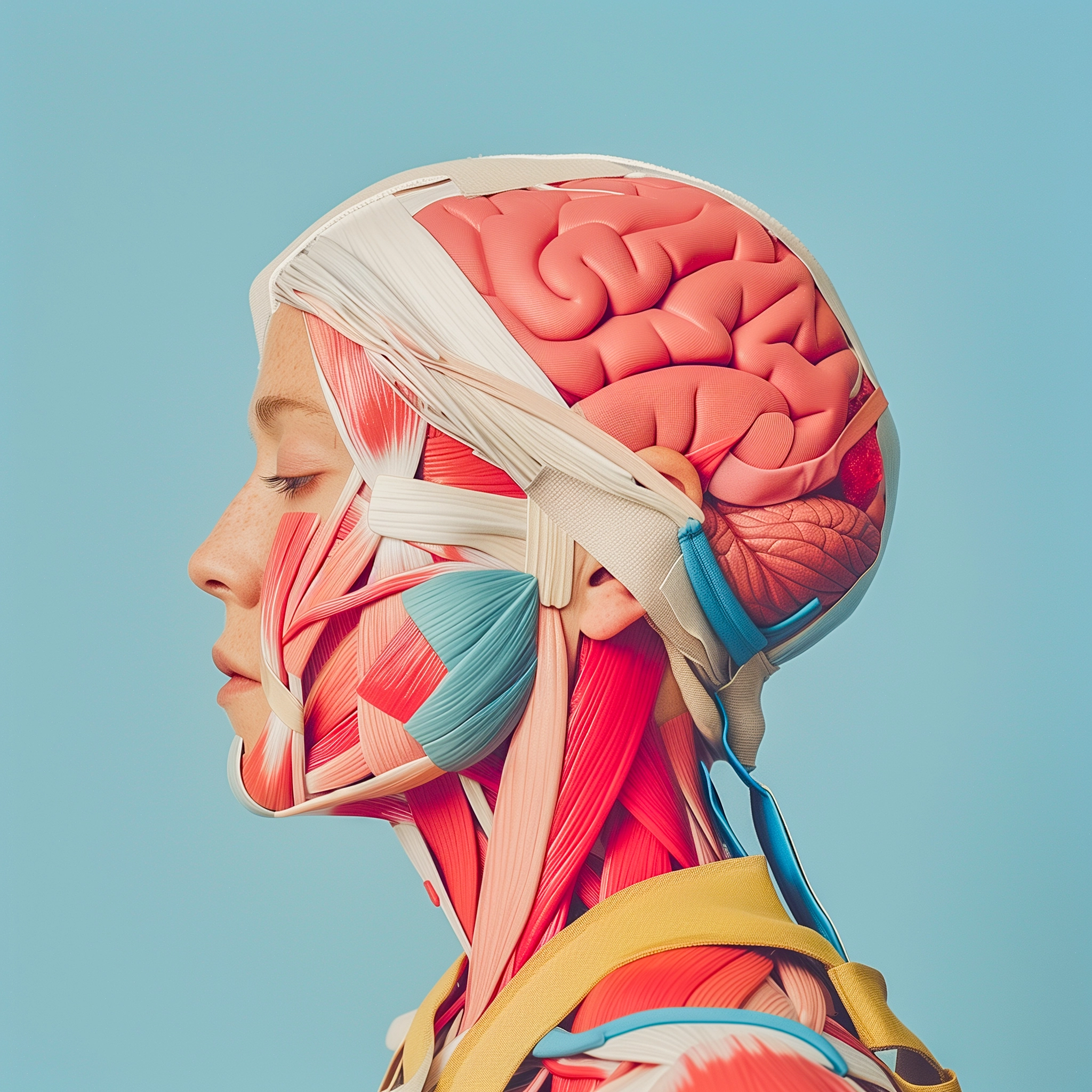
Science
Human Anatomy
The study of the structure of the human body and its parts.
Human anatomy is the branch of biology that focuses on the structural organization of the human body. It examines the body's physical composition, from the smallest cellular structures to larger systems that work together to support life. Human anatomy is traditionally divided into two main areas: gross anatomy, which looks at the larger structures visible to the naked eye (like organs and bones), and microscopic anatomy (or histology), which studies tissues and cells at the microscopic level. The body is organized into various systems, such as the skeletal, muscular, circulatory, and nervous systems, each with specific functions that maintain overall health and homeostasis. Understanding human anatomy is essential for medical science, physiology, and understanding how the body works, responds to stimuli, and heals after injury. Anatomy forms the foundation for fields like medicine, physiotherapy, and biological research, offering crucial insights into both normal and abnormal functions of the human body.
Organs
Specialized body structures that perform specific vital functions.
Anus
The terminal opening of the digestive tract, crucial for the expulsion of feces.
Appendix
A small, tube-like structure attached to the large intestine.
Bladder
A hollow muscular organ that stores urine until it is ready to be excreted from the body.
Brain
The complex organ that serves as the control center of the body, overseeing thoughts, movements, emotions, and sensory processing.
Bronchi
The air passages that branch from the trachea and lead directly to the lungs.
Cervix
A narrow passage connecting the uterus to the vagina, playing a vital role in female reproductive health.
Duodenum
The first section of the small intestine that plays a key role in digestion.
Ears
The organs that play a crucial role in hearing and balance.
Epididymis
A coiled tubular structure responsible for the maturation and storage of sperm cells.
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach, facilitating the passage of food and liquids.
Eyes
The organs responsible for vision, enabling the perception of light and color.
Fallopian tubes
These delicate tubes play a crucial role in the female reproductive system.
Gallbladder
A small organ that plays a crucial role in digesting fats and storing bile.
Heart
A muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body and maintaining circulation.
Ileum
The final section of the small intestine, critical for nutrient absorption and digestion.
Jejunum
A vital section of the small intestine that plays a central role in nutrient absorption.
Kidneys
An essential organ involved in filtering blood, regulating blood pressure, and maintaining electrolyte balance.
Large intestine
A critical component of the digestive system that absorbs water, electrolytes, and processes waste material.
Larynx
The structure essential for voice production and protection of the airway.
Liver
The largest internal organ in the body, crucial for various metabolic processes and detoxification.
Lungs
The vital organs responsible for gas exchange, allowing the intake of oxygen and the expulsion of carbon dioxide.
Lymph nodes
Small, bean-shaped structures that play a crucial role in the immune system.
Mouth
The entry point for food and air, playing a crucial role in digestion and speech.
Nose
The prominent structure on the face responsible for breathing, filtering air, and sensing smell.
Penis
The male reproductive organ responsible for sexual intercourse and the delivery of sperm.
Pharynx
A muscular tube that plays a crucial role in both the respiratory and digestive systems.
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine, it plays a crucial role in the digestive system and waste elimination.
Skin
The largest organ of the body, serving as a protective barrier and regulating temperature.
Small intestine
A vital organ responsible for the majority of nutrient absorption and digestion in the body.
Spleen
An organ that plays a vital role in immune function and blood filtration.
Stomach
A muscular organ crucial for digesting food and aiding in nutrient absorption.
Tongue
A muscular organ essential for taste, manipulating food, and aiding in speech.
Tonsils
These lymphoid tissues play a crucial role in the immune system, guarding the entry points of the body.
Trachea
The tube that serves as the main airway, allowing air to flow to and from the lungs.
Ureters
The tubes responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Urethra
A tube responsible for the passage of urine and, in males, semen out of the body.
Uterus
An essential reproductive organ that plays a crucial role in supporting fetal development during pregnancy.
Vagina
The muscular canal that connects the external genitals to the uterus.
Vas deferens
A muscular tube that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
Bones
Rigid structures that form the skeleton and provide support and protection to the body.
Calcaneus
The largest bone in the foot, primarily connecting the foot to the ground and facilitating mobility.
Capitate
A large bone in the wrist that plays a crucial role in hand movement and stability.
Carpals
The group of small bones that make up the wrist and connect the hand to the forearm.
Clavicle
A long bone that connects the arm to the body and serves as a support structure for the shoulder.
Coccyx
A small, triangular bone at the base of the vertebral column, often referred to as the tailbone.
Cuboid
A wrist bone that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of the foot.
Cuneiform bones
The group of three small bones located in the foot, essential for proper movement and support.
Ethmoid bone
A key structure within the skull that contributes to the formation of the nasal cavity and the orbits of the eyes.
Femur
The longest and strongest bone in the human body, crucial for supporting body weight and facilitating movement.
Fibula
A slender bone located in the lower leg, playing a key role in stabilization and support.
Frontal bone
The frontal bone forms the anterior part of the skull and contributes to the shape of the forehead.
Hamate
A wrist bone shaped like a hook, contributing to the structure and function of the hand.
Humerus
A long bone in the upper arm that connects the shoulder to the elbow.
Hyoid bone
A unique U-shaped bone that serves as an anchor point for the tongue and various muscles in the neck.
Ilium
A large, flat bone on each side of the pelvic region, playing a crucial role in supporting the body's structure.
Incus
A small bone located in the middle ear, crucial for the process of hearing.
Inferior nasal conchae
These bony structures located within the nasal cavity play a crucial role in the respiratory process.
Ischium
A key component of the pelvis that provides structural support and serves as a site for muscle attachment.
Lacrimal bones
Small, thin bones located in the inner corner of the eye sockets.
Lunate
A crescent-shaped bone located in the wrist that plays a critical role in wrist movement and stability.
Malleus
A small bone located in the middle ear, critical for the process of hearing.
Mandible
The largest and strongest bone in the human face, it holds the lower teeth and forms the jawline.
Maxilla
The bone that forms the upper jaw and holds the upper teeth, contributing to the structure of the face.
Metacarpals
The long bones in the hand that connect the wrist to the fingers.
Metatarsals
These long bones form the intermediate part of the foot structure, connecting the ankle to the toes.
Nasal bones
Small, paired bones that form the bridge of the nose.
Navicular
A bone situated in the foot that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of the ankle.
Occipital bone
A crucial structure of the skull that houses the brain and supports the spinal column.
Palatine bones
These paired bones form a portion of the hard palate and contribute to the structure of the oral cavity.
Parietal bones
Two large, flat bones situated on the sides and roof of the skull.
Patella
A small, flat bone located in the front of the knee joint.
Pelvis
A complex structure that supports the weight of the upper body and plays a crucial role in locomotion.
Phalanges
The bones that make up the fingers of the hands and the toes of the feet.
Pisiform
A small, pea-shaped bone located in the wrist, contributing to its complex structure.
Pubis
A key component of the pelvic bone structure, playing a crucial role in forming the hip joint and supporting the body.
Radius
A long bone located in the forearm, playing a critical role in arm movement and stability.
Ribs
The curved bones that form the rib cage, providing structure and protection to the thoracic organs.
Sacrum
A triangular bone located at the base of the spine, forming the posterior aspect of the pelvis.
Scaphoid
A small bone in the wrist that plays a crucial role in hand mobility and stability.
Scapula
A flat triangular bone that forms a vital connection between the arm and the trunk of the body.
Sesamoid bones
Small, round bones embedded within tendons that help to increase the mechanical advantage of muscles.
Skull
The bony structure that encases and protects the brain while providing support for the face.
Sphenoid bone
A complex bone situated at the base of the skull, known for its butterfly-like shape.
Stapes
The smallest bone in the human body, vital for transmitting sound waves.
Sternum
A flat bone located in the center of the chest, connecting to the ribs and providing structure to the ribcage.
Talus
A crucial bone in the ankle joint that facilitates movement and bears weight.
Tarsals
The group of bones that compose the ankle and the proximal part of the foot.
Temporal bones
Pair of bones that form parts of the side of the skull and surround the ear.
Tibia
A crucial bone that supports weight and facilitates movement in the lower leg.
Trapezium
A carpal bone located in the wrist that plays a vital role in thumb movement.
Trapezoid
A small, complex bone located in the wrist, important for wrist stability and movement.
Triquetrum
A small, pyramid-shaped bone located in the wrist that plays a crucial role in wrist function and stability.
Ulna
A long bone located in the forearm, stretching from the elbow to the wrist on the inner side of the arm.
Vertebrae
The individual bones that make up the vertebral column, which supports the body and encases the spinal cord.
Vomer
A thin, flat bone forming the posterior portion of the nasal septum.
Zygomatic bones
Facial bones that contribute to the structure of the cheeks and the orbit of the eyes.
Muscles
Tissues that contract to produce movement in the body.
Adductor brevis
A muscle located in the inner thigh, crucial for moving the leg inward toward the body.
Adductor longus
A prominent muscle located in the inner thigh, essential for leg movement and stabilization.
Adductor magnus
A large muscle of the inner thigh that plays a crucial role in leg movement and stability.
Biceps brachii
A prominent muscle located in the upper arm, crucial for various arm movements.
Brachialis
A muscle located in the upper arm, playing a crucial role in flexing the elbow.
Brachioradialis
A muscle located in the forearm, primarily involved in the flexion of the elbow.
Buccinator
A muscle situated in the cheek, playing a crucial role in facial expressions and oral functions.
Bulbospongiosus
A muscle that plays a critical role in both the male and female reproductive systems.
Coccygeus
A muscle located at the base of the pelvic floor, contributing to pelvic support.
Deltoid
A key muscle responsible for shoulder abduction, flexion, and rotation of the arm.
Depressor anguli oris
A muscle that plays a key role in facial expressions, particularly in frowning and the downward movement of the corners of the mouth.
Diaphragm
The dome-shaped muscle that plays a crucial role in respiration.
Erector spinae
A crucial group of muscles responsible for maintaining posture and stability of the spine.
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
A muscle located in the forearm, responsible for extending and abducting the wrist.
Extensor carpi radialis longus
A muscle located in the forearm that plays a vital role in wrist movement.
Extensor carpi ulnaris
A muscle located in the forearm that primarily facilitates wrist extension and ulnar deviation.
Extensor digitorum
A muscle crucial for the extension of the fingers and the wrist.
Extensor digitorum longus
A muscle located in the anterior compartment of the leg that is integral to extending the toes.
Extensor hallucis longus
A muscle responsible for extending the big toe and aiding in dorsiflexion of the foot.
Extensor muscles
A group of muscles responsible for extending joints and straightening limbs.
External obliques
A key muscle group involved in trunk movement, rotation, and stability.
Flexor carpi radialis
A muscle that flexes and abducts the wrist, contributing to hand movements.
Flexor carpi ulnaris
A muscle that plays a crucial role in wrist movement and stability.
Flexor digitorum longus
A muscle that plays a crucial role in the movement and function of the toes.
Flexor digitorum profundus
A muscle critical for finger flexion and grip strength.
Flexor digitorum superficialis
This muscle functions primarily to flex the fingers and is crucial for grasping and holding objects.
Flexor hallucis longus
A muscle located in the posterior compartment of the leg, primarily responsible for flexing the big toe.
Flexor muscles
Muscles responsible for bending joints and reducing the angle between body parts.
Gastrocnemius
A major calf muscle involved in movement and stability, particularly during walking, running, and jumping.
Gemellus inferior
A small muscle located in the gluteal region, playing a vital role in hip movements.
Gemellus superior
A muscle located in the posterior region of the hip, playing a crucial role in hip movement.
Gluteus maximus
The largest muscle in the human body, crucial for movement and stability.
Gluteus medius
A key muscle in the hip region, playing a crucial role in movement and stability.
Gluteus minimus
A small yet vital muscle located in the hip region, contributing to movement and stability.
Gracilis
A long, slender muscle located in the inner thigh, playing a role in leg movement.
Hamstrings
A group of muscles located at the back of the thigh essential for movement and stability.
Hypothenar muscles
A group of muscles located in the palm that primarily function to control the movements of the little finger.
Iliopsoas
A powerful muscle group essential for hip flexion and maintaining posture.
Inferior oblique
A muscle that plays a crucial role in the movement of the eye.
Inferior rectus
A muscle responsible for downward eye movement and assists in rotation.
Infraspinatus
A muscle that plays a crucial role in shoulder movement and stability.
Intercostal muscles
Muscles located between the ribs that play a vital role in breathing.
Internal obliques
A pair of muscles located on the lateral sides of the abdomen, playing a crucial role in trunk movement and stability.
Interossei muscles
Muscles located in the hands and feet that play a crucial role in fine motor skills and balance.
Ischiocavernosus
A muscle that plays a significant role in erectile function.
Lateral rectus
A muscle that plays a crucial role in the movement of the eye.
Latissimus dorsi
A large, flat muscle that spans the lower back and contributes to various movements of the shoulder and torso.
Levator ani
A group of muscles that provide support to the pelvic organs and aid in maintaining continence.
Levator labii superioris
A muscle responsible for elevating the upper lip and assisting in facial expressions.
Levator scapulae
A muscle that elevates the scapula and assists in neck movements.
Lumbricals
Small, worm-like muscles located in the hand and foot.
Masseter
A strong muscle responsible for elevating the jaw during chewing.
Medial rectus
The muscle responsible for controlling the movement of the eye towards the nose.
Mentalis
A pair of muscles located in the chin that contribute to facial expressions.
Multifidus
A group of deep spine muscles that play a vital role in stabilizing the vertebral column.
Obturator externus
A muscle located in the hip region that plays a vital role in the movement and stability of the thigh.
Obturator internus
A muscle located in the pelvis, playing a key role in the movement of the hip joint.
Occipitofrontalis
A muscle critical for facial expression, particularly in raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead.
Orbicularis oculi
Muscle responsible for closing the eyelids and surrounding the eye.
Orbicularis oris
A complex muscle that encircles the mouth, vital for various facial movements.
Palmaris longus
A muscle located in the forearm that plays a role in wrist flexion.
Pectineus
A muscle located in the upper thigh, responsible for hip flexion and adduction.
Pectoralis major
A large muscle located in the upper chest, crucial for arm movement and stability.
Pectoralis minor
A thin, triangular muscle located in the upper chest area, contributing to shoulder movement.
Peroneus brevis
A muscle located in the lower leg, playing a crucial role in foot movement and stability.
Peroneus longus
A muscle that plays a crucial role in stabilizing the ankle and facilitating various movements of the foot.
Peroneus muscles
The group of muscles responsible for the eversion of the foot and providing stability during movement.
Piriformis
A muscle located in the gluteal region that plays a crucial role in hip movement and stability.
Plantaris
A small muscle located in the posterior compartment of the leg, it plays a role in plantarflexion of the foot.
Platysma
A thin, superficial muscle that covers the front of the neck and extends to the lower jaw and chest.
Popliteus
A small, triangular muscle located at the back of the knee joint.
Pronator quadratus
A small, square-shaped muscle located in the forearm.
Pronator teres
A muscle in the forearm responsible for pronation, which turns the palm downward.
Pyramidalis
A small, triangular muscle located in the lower abdominal region.
Quadratus femoris
A flat, quadrilateral muscle located in the hip region.
Quadratus lumborum
A quadrilateral muscle situated in the lower back, vital for spinal stability and movement.
Quadriceps femoris
A powerful muscle group crucial for knee extension and mobility.
Rectus abdominis
A pair of muscles located in the anterior abdominal wall, playing a key role in core stability and motion.
Rhomboids
Muscles that play a crucial role in the movement and stabilization of the shoulder blades.
Sartorius
A long, strap-like muscle that runs across the front of the thigh.
Serratus anterior
A muscle that plays a crucial role in shoulder movement and upper limb stability.
Soleus
A powerful muscle located in the lower leg, playing a crucial role in standing and walking.
Sphincter urethrae
A cylindrical muscle that plays a crucial role in urine control and the regulation of urine flow.
Sternocleidomastoid
A key muscle in the neck that plays a vital role in head movement and rotation.
Subscapularis
A key muscle located in the shoulder, it plays a critical role in arm movement and stabilization.
Superior oblique
A muscle that plays a vital role in the movement of the eye.
Superior rectus
A muscle responsible for elevating the eye and assisting in its inward rotation.
Supinator
A muscle facilitating the outward rotation of the forearm and hand.
Supraspinatus
A muscle located in the shoulder, crucial for arm movement and stabilization.
Temporalis
A muscle that plays a crucial role in the movement of the jaw.
Tensor fasciae latae
A muscle located on the outer side of the thigh that plays a key role in the stabilization of the hip and knee.
Teres minor
A small, yet crucial muscle located in the shoulder region.
Thenar muscles
A group of muscles located at the base of the thumb, responsible for its movement and dexterity.
Tibialis anterior
A muscle located in the front part of the lower leg, crucial for foot movement and stability.
Transverse abdominis
A vital core muscle that plays a crucial role in stabilizing the pelvis and spine.
Transversus thoracis
A thin muscle located in the chest wall that plays a role in respiration.
Trapezius
A large, triangular muscle that extends from the back of the neck to the middle of the back and creates a triangular shape.
Triceps brachii
A large muscle located at the back of the upper arm that plays a significant role in arm movement and strength.
Vastus intermedius
A key muscle located in the thigh, playing an essential role in knee extension.
Vastus lateralis
A powerful muscle located in the thigh, crucial for movement and stability.
Vastus medialis
A muscle located in the front of the thigh, crucial for knee extension and stabilization.
Zygomaticus major
A muscle that plays a key role in facial expression, particularly in smiling.
Zygomaticus minor
A facial muscle that plays a significant role in the expression of emotions.
Arteries and Veins
Blood vessels responsible for carrying blood to and from the heart.
Abdominal aorta
The major blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the lower half of the body.
Anterior cerebral artery
A crucial blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the medial portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes.
Anterior tibial artery
A major blood vessel responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to the front part of the lower leg.
Anterior tibial vein
A crucial blood vessel responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the lower leg and foot.
Aorta
The largest artery in the body, responsible for transporting oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Axillary artery
A major blood vessel that supplies blood to the upper limb and shoulder region.
Axillary vein
A major blood vessel responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the upper limb.
Azygos vein
A vital component of the venous system, the azygos vein is crucial for draining blood from the thorax and abdomen.
Basilic vein
A major vein in the upper limb that drains blood from the forearm and part of the hand.
Brachial artery
The primary artery supplying blood to the upper arm, branching off from the axillary artery.
Brachial vein
A major blood vessel that drains deoxygenated blood from the upper limb and returns it to the heart.
Carotid arteries
Major blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the head and neck.
Celiac trunk
A major artery that supplies blood to the upper abdominal organs.
Cephalic vein
A prominent vein that plays a vital role in draining blood from the upper limb.
Cerebral arteries
The critical vessels that supply blood to the brain, ensuring it receives the oxygen and nutrients necessary for proper function.
Cerebral veins
The network of blood vessels responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the brain.
Coronary arteries
The blood vessels responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
Deep femoral artery
A major artery that plays a crucial role in supplying blood to the thigh region.
Deep femoral vein
A major vein that drains blood from the thigh muscles into the femoral vein.
Digital arteries
Small blood vessels responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to the fingers and toes.
Digital veins
The structures responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the fingers and toes back to the heart.
Dorsal venous arch
A network of veins located on the top of the foot, serving as a critical channel for blood drainage.
Dorsalis pedis artery
A vital artery supplying blood to the upper surface of the foot.
External carotid artery
A major artery supplying blood to the face and neck.
External iliac artery
A major blood vessel responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to the lower limbs and pelvis.
External iliac vein
A major blood vessel that drains deoxygenated blood from the lower limbs and pelvis back to the heart.
External jugular vein
A major vein that drains blood from the head and neck.
Facial artery
An important blood vessel supplying the face and neck with oxygenated blood.
Facial vein
A major vein that plays a crucial role in draining deoxygenated blood from the face.
Femoral artery
A major blood vessel responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to the thigh and lower leg.
Femoral vein
A major blood vessel responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the thigh and lower leg back to the heart.
Fibular artery
A vital blood vessel supplying the lateral compartment of the leg.
Fibular vein
A vital vessel that plays a key role in the circulation of blood in the lower leg.
Gonadal arteries
These arteries supply blood to the reproductive organs, playing a crucial role in sexual health.
Gonadal veins
The vessels responsible for draining blood from the gonads, which are the reproductive organs in both males and females.
Great saphenous vein
The longest vein in the body, running down the length of the leg.
Hemiazygos vein
A vein that plays a crucial role in draining blood from the thorax and abdomen.
Hepatic artery
A vital blood vessel that supplies oxygen-rich blood to the liver.
Hepatic veins
The blood vessels responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the liver and returning it to the heart.
Iliac arteries
Crucial blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the lower limbs and pelvic region.
Iliac veins
The vessels that transport deoxygenated blood from the lower limbs and pelvis back to the heart.
Inferior mesenteric artery
A critical blood vessel supplying the lower part of the intestines.
Inferior sagittal sinus
A major venous channel located within the brain that plays a crucial role in draining blood.
Inferior vena cava
The large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart.
Internal carotid artery
This vital blood vessel supplies oxygenated blood to the brain, neck, and face.
Internal iliac artery
A major vessel supplying blood to the pelvic region and the lower limbs.
Internal iliac vein
A major vessel responsible for draining blood from the pelvic region and gluteal muscles.
Internal jugular vein
A major vein that drains blood from the head and neck regions and returns it to the heart.
Jugular veins
Major veins that drain blood from the head and neck region back to the heart.
Lingual artery
A key vessel supplying blood to the tongue and floor of the mouth.
Maxillary artery
A major blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to various structures of the face and oral cavity.
Median cubital vein
A key superficial vein located in the forearm, predominantly involved in venous blood collection.
Mesenteric arteries
The arteries that supply blood to the intestines, essential for nutrient absorption and digestion.
Mesenteric veins
Veins that drain deoxygenated blood from the intestines back to the heart.
Middle cerebral artery
A major blood vessel that supplies essential blood to key areas of the brain, particularly those responsible for motor and sensory functions.
Occipital artery
A crucial vessel supplying blood to the posterior region of the head.
Ophthalmic artery
A vital vessel supplying blood to the eye and its surrounding structures.
Ophthalmic veins
Veins responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the eye and surrounding structures.
Palmar arches
A network of blood vessels supplying the hand, crucial for maintaining healthy circulation in the fingers.
Palmar venous arches
The network of veins that drains blood from the palm of the hand.
Popliteal artery
A critical vessel that supplies blood to the lower leg and foot.
Popliteal vein
A significant vein responsible for draining blood from the lower leg and knee region back to the heart.
Portal vein
The major vessel that transports blood from the gastrointestinal tract and spleen to the liver.
Posterior cerebral artery
A key vessel supplying oxygenated blood to the brain, specifically the occipital lobe and parts of the temporal lobe.
Posterior tibial artery
A crucial blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the lower leg and foot.
Posterior tibial vein
A crucial vessel that drains deoxygenated blood from the lower leg and foot back to the heart.
Pulmonary arteries
Vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Radial artery
A major artery of the forearm that supplies blood to the hand and wrist.
Radial vein
A crucial vessel involved in returning deoxygenated blood from the forearm to the heart.
Renal arteries
Vessels that supply blood to the kidneys, essential for their function in filtering waste from the blood.
Renal veins
The vessels responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys.
Sigmoid sinus
A key venous channel responsible for draining blood from the brain.
Small saphenous vein
A significant vein that drains blood from the lower limb towards the heart.
Straight sinus
A major venous channel located within the cranial cavity.
Subclavian arteries
Vital arteries that supply blood to the upper limbs and parts of the neck.
Subclavian veins
The veins that play a crucial role in draining blood from the upper limbs and parts of the neck.
Superficial temporal artery
A vital blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the side of the head and face.
Superior mesenteric artery
A major blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the intestines.
Superior sagittal sinus
A major venous channel located within the brain's dural layers.
Superior vena cava
A large vein responsible for transporting deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart.
Thoracic aorta
A major artery that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Transverse sinus
A blood-filled channel located within the brain's dura mater.
Ulnar artery
This major blood vessel primarily supplies blood to the medial aspect of the forearm and hand.
Ulnar vein
A blood vessel that plays a crucial role in returning deoxygenated blood from the forearm to the heart.
Vertebral artery
A major artery that supplies blood to the brain and spinal cord.
Nerves
Bundles of fibers that transmit signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body.
Abducens nerve
A cranial nerve primarily responsible for eye movement.
Accessory nerve
A cranial nerve that plays a vital role in neck and shoulder movement.
Ansa cervicalis
A loop of nerves located in the neck that plays a crucial role in the innervation of certain neck muscles.
Axillary nerve
A crucial nerve responsible for innervating the deltoid and teres minor muscles, as well as providing sensory function to the skin over the lateral aspect of the shoulder.
Brachial plexus
A network of nerves that supplies the upper limb and provides motor and sensory innervation to the shoulder, arm, and hand.
Cervical plexus
A network of nerves located in the neck region that plays a crucial role in sensory and motor function.
Coccygeal plexus
A network of nerves found in the pelvic region, responsible for innervating the skin and muscles in the area around the tailbone.
Common peroneal nerve
A critical nerve responsible for motor and sensory functions in the leg and foot.
Deep fibular nerve
A crucial nerve responsible for motor and sensory functions in the lower leg and foot.
Facial nerve
A critical nerve that controls the muscles of facial expression and carries sensory information from the taste buds.
Femoral nerve
A major nerve in the thigh that primarily controls movement and sensation in the anterior compartment of the thigh.
Genitofemoral nerve
A mixed nerve responsible for sensation in the groin and motor function to certain muscles in the lower abdomen.
Glossopharyngeal nerve
A cranial nerve that plays a crucial role in taste, swallowing, and autonomic functions.
Hypoglossal nerve
A cranial nerve primarily responsible for controlling tongue movements.
Iliohypogastric nerve
A key nerve responsible for sensation and motor control in the lower abdominal region.
Ilioinguinal nerve
A nerve that plays a crucial role in providing sensory and motor innervation to the lower abdomen and groin region.
Inferior gluteal nerve
A vital nerve that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle, influencing lower limb movement and stability.
Intercostal nerves
A series of nerves that play a crucial role in the sensory and motor functions of the thoracic region.
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
A nerve that provides sensation to the skin on the outer thigh.
Long thoracic nerve
A critical nerve that plays a pivotal role in shoulder movement and stability.
Lumbar plexus
A network of nerves that provides motor and sensory innervation to parts of the lower back, pelvis, and lower limb.
Median antebrachial cutaneous nerve
A sensory nerve that provides sensation to the skin of the forearm.
Median nerve
A critical nerve in the arm responsible for sensation and movement in certain hand areas.
Musculocutaneous nerve
A critical nerve that plays a vital role in both motor and sensory functions of the upper limb.
Obturator nerve
A critical nerve that facilitates movement and sensation in the inner thigh and associated areas.
Oculomotor nerve
A cranial nerve primarily responsible for eye movement and several key functions in ocular health.
Olfactory nerve
A vital component of the sensory system, this nerve is primarily responsible for the sense of smell.
Optic nerve
The structure responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain.
Phrenic nerve
The nerve that plays a crucial role in the control of breathing and diaphragm movement.
Plantar nerves
Nerves that provide sensation and motor control to the foot's sole.
Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
A key nerve responsible for sensation in the posterior thigh and part of the gluteal region.
Pudendal nerve
A crucial nerve responsible for sensation and motor function in the pelvic region.
Radial nerve
A crucial nerve that enables movement and sensation in the arm and hand.
Sacral plexus
A network of nerves located in the lower back, crucial for innervating the pelvis and lower limbs.
Saphenous nerve
A major sensory nerve of the leg that plays a vital role in innervating the skin of the lower limb.
Sciatic nerve
A crucial nerve that extends from the lower back down each leg, providing movement and sensation.
Spinal cord
A crucial structure that enables communication between the brain and the body, playing a key role in the nervous system.
Superficial fibular nerve
A branch of the common fibular nerve, crucial for sensation in the lower leg and foot.
Superior gluteal nerve
A crucial nerve responsible for motor function in the gluteal region and the stability of the hip joint.
Sural nerve
A critical nerve that supplies sensation to the back of the lower leg and the lateral aspect of the foot.
Tibial nerve
A critical nerve responsible for sensation and motor function in the lower leg and foot.
Trigeminal nerve
A crucial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as chewing.
Trochlear nerve
A critical component in eye movement and orientation.
Ulnar nerve
The ulnar nerve is a crucial nerve responsible for movement and sensation in the forearm and hand.
Vagus nerve
A crucial nerve that plays a key role in regulating the autonomic nervous system and connecting the brain to various organs.
Vestibulocochlear nerve
A crucial nerve responsible for transmitting sound and balance information from the inner ear to the brain.
Glands
Organs that produce and release substances like hormones or enzymes.
Adrenal glands
Small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of each kidney that produce hormones essential for regulating metabolism and stress response.
Bartholin's glands
Pair of glands located on either side of the vaginal opening, responsible for secreting fluid that aids in lubrication.
Brunner's glands
Glands responsible for producing a fluid that protects the intestinal lining and aids in digestion.
Bulbourethral glands
Glands that produce a pre-ejaculate fluid that lubricates the urethra and neutralizes acidity.
Ceruminous glands
Secretory glands in the ear that produce earwax, contributing to ear health and hygiene.
Ciliary glands
Small glands located in the eyelids that contribute to eye moisture.
Gastric glands
Structures located in the lining of the stomach that produce gastric juices.
Glands of Montgomery
These glands play a crucial role in lactation and breast health.
Glands of Zeis
Small sebaceous glands located on the margins of the eyelids, responsible for lubrication.
Hypothalamus
A crucial brain region that regulates numerous bodily functions, including temperature, hunger, and sleep.
Intestinal glands
Glands within the intestinal lining that play a crucial role in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Islets of Langerhans
Clusters of cells within the pancreas that play a vital role in hormone production.
Juxtaglomerular cells
These specialized cells play a critical role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining fluid balance.
Lacrimal glands
Small glands located in the upper outer corner of each eye, responsible for producing tears.
Mammary glands
Glands that produce milk in female mammals for feeding their young.
Meibomian glands
These glands are responsible for secreting oils that prevent the evaporation of the tear film on the eye's surface.
Ovaries
The female reproductive organs responsible for the production of eggs and hormones.
Pancreas
An essential gland that plays a crucial role in digestion and blood sugar regulation.
Parathyroid glands
Small glands that play a crucial role in regulating calcium levels in the blood.
Parotid glands
The largest salivary glands, critical for the production and secretion of saliva.
Peyer's patches
Small lymphatic tissues found in the small intestine that play a vital role in immune surveillance.
Pineal gland
A small endocrine gland responsible for producing melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Pituitary gland
A pea-sized gland often referred to as the 'master gland' of the endocrine system.
Placenta
An essential organ that develops during pregnancy, facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste between the mother and fetus.
Prostate gland
A small gland located just below the bladder that plays a crucial role in male reproductive health.
Salivary glands
Glands located in and around the mouth that produce saliva to aid in digestion and oral health.
Sebaceous glands
Small glands in the skin that secrete an oily substance called sebum.
Seminal vesicles
The glands that produce a significant portion of the fluid that nourishes and helps transport sperm.
Skene's glands
The glands located near the female urethra that play a role in sexual function and lubrication.
Sublingual glands
Salivary glands located beneath the tongue that play a crucial role in digestion and oral health.
Submandibular glands
Salivary glands located beneath the jaw that play a crucial role in digestion and oral health.
Sweat glands
The glands responsible for the production and secretion of sweat, which helps regulate body temperature.
Testes
The paired organs responsible for producing sperm and hormones like testosterone.
Thymus gland
A vital organ involved in the development of the immune system, particularly T-cells.
Thyroid gland
A butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, responsible for regulating metabolism and hormone production.
Von Ebner's glands
Salivary glands located at the back of the tongue, playing a key role in oral health and taste.
Cartilage
Flexible connective tissue found in various parts of the body such as joints, ears, and nose.
Annulus fibrosus
A tough, fibrous outer ring of the intervertebral discs in the spine.
Articular cartilage
A specialized tissue that covers the ends of bones in synovial joints, facilitating smooth movement and absorbing shock.
Articular discs
These are fibrocartilaginous structures that improve the fit between joint surfaces and enhance stability.
Arytenoid cartilages
Small, paired cartilages located in the larynx that play a crucial role in voice production and breathing.
Bronchial cartilage
A vital component of the respiratory system, providing structure and support to the bronchial tubes.
Corniculate cartilages
Small, horn-shaped cartilages that form part of the laryngeal structure.
Costal cartilage
Connects the ribs to the sternum, contributing to the structure of the rib cage.
Costal cartilage of the xiphoid process
The structure that connects the xiphoid process to the rib cage, providing flexibility and support.
Cricoid cartilage
A crucial component of the laryngeal structure, providing support and protection for the airway.
Cuneiform cartilages
Small cartilaginous structures situated in the larynx that play a role in vocal cord function.
Ear cartilage
A flexible connective tissue that shapes and supports the outer ear.
Epiglottis
A critical flap of tissue that plays a vital role in protecting the airway during swallowing.
Epiphyseal plate cartilage
The region of growing tissue located at the ends of long bones, facilitating bone growth in length during development.
Fibrocartilage of the pubic symphysis
The fibrocartilage of the pubic symphysis serves as a resilient cushioning structure between the pelvic bones.
Intervertebral discs
Discs that act as cushions between the vertebrae of the spinal column.
Laryngeal cartilage
A critical structure that provides support and shape to the larynx, which plays a vital role in voice production and airway protection.
Meniscus
A crescent-shaped cartilage structure in the knee joint that provides cushioning and stability.
Nasal cartilage
A flexible structure that shapes and supports the nose.
Septal cartilage
A flexible structure that forms the framework of the nasal septum, separating the nasal cavities.
Thyroid cartilage
The largest cartilage of the larynx, crucial in protecting the vocal cords.
Tracheal cartilage
The supportive structure that helps maintain the airway's openness and flexibility.
Tissues
Groups of cells that work together to perform specific functions.
Adipose tissue
A type of connective tissue that stores energy in the form of fat and provides insulation and cushioning for the body.
Areolar connective tissue
A type of loose connective tissue that provides support and elasticity to various organs.
Blood tissue
A connective tissue vital for transporting nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Bone tissue
A specialized form of connective tissue that provides structural support and protection to the body.
Cardiac muscle tissue
A specialized muscle type responsible for the contraction of the heart, enabling circulation.
Cartilage tissue
A flexible connective tissue that provides support and cushioning in various parts of the body.
Connective tissue
A diverse group of tissues that support, bind, and protect other tissues and organs throughout the body.
Dense irregular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that provides strength, elasticity, and support to various organs and structures in the body.
Dense regular connective tissue
A vital tissue that provides strength and support through tightly packed collagen fibers.
Elastic connective tissue
A specialized form of connective tissue that provides elasticity and resilience to various structures in the body.
Elastic tissue
A specialized connective tissue that provides elasticity and flexibility to various organs and structures in the body.
Endothelial tissue
A specialized type of tissue that lines the interior surfaces of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
Epithelial tissue
A type of tissue that forms the protective outer layer of the body and lines organs and cavities.
Fibrous tissue
A connective tissue that provides support and structure throughout the body.
Gray matter
A crucial component of the central nervous system, involved in processing information and executing commands.
Hematopoietic tissue
The specialized tissue responsible for the production of blood cells and the maintenance of the body's immune system.
Lymphoid tissue
A vital component of the immune system, which assists in the production and maturation of immune cells.
Mesenchymal tissue
A type of connective tissue that plays a crucial role in the development and repair of other tissues.
Mesothelial tissue
A type of epithelial tissue that lines body cavities and covers organs.
Mucous connective tissue
A type of connective tissue rich in mucopolysaccharides that provides support and flexibility.
Muscle tissue
A specialized tissue responsible for facilitating movement in the body.
Nervous tissue
A specialized tissue responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body, allowing for communication between different body parts.
Neuroglia
Cells that support, nourish, and protect neurons in the nervous system.
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
A specialized type of epithelial tissue that appears to be layered due to differing cell heights.
Reticular tissue
A type of connective tissue that provides a supportive framework for various organs in the body.
Simple columnar epithelium
A type of tissue characterized by a single layer of tall, column-shaped cells that perform various vital functions.
Simple cuboidal epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue that is composed of a single layer of cube-shaped cells.
Simple squamous epithelium
A type of epithelium that consists of a single layer of flat cells, primarily involved in filtration and diffusion.
Skeletal muscle tissue
A type of muscle tissue that enables voluntary movement of the body.
Smooth muscle tissue
A type of involuntary muscle that plays a critical role in various organ systems throughout the body.
Stratified columnar epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue characterized by multiple layers of tall, column-like cells.
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
A type of tissue composed of multiple layers of cube-shaped cells.
Stratified squamous epithelium
A multi-layered tissue that protects underlying structures from abrasion, pathogens, and chemical exposure.
Synovial membranes
The thin layer of tissue that lines the cavities of joints, providing lubrication and nourishment to the cartilage.
Transitional epithelium
A specialized type of tissue that stretches and changes shape to accommodate variations in volume.
White matter
The type of neural tissue that facilitates communication between different regions of the brain and spinal cord.
Joints
Locations where bones meet, allowing for movement and support.
Acromioclavicular joint
The joint connecting the collarbone to the highest point of the shoulder blade.
Ankle joint
The joint connecting the foot to the leg, allowing for movement and weight-bearing actions.
Atlanto-occipital joint
A critical joint connecting the skull to the spine, facilitating head movement and stability.
Atlantoaxial joint
A pivotal joint located between the first and second cervical vertebrae that enables a range of head movements.
Carpometacarpal joints
The joints that connect the carpal bones of the wrist to the metacarpal bones of the hand.
Costochondral joints
These joints connect the ribs to the costal cartilages, contributing to the flexibility of the rib cage.
Costovertebral joints
Key structures that connect the ribs to the spine, enabling thoracic movement and stability.
Cricoarytenoid joint
A pivotal joint in the larynx involved in voice production and airway regulation.
Cricothyroid joint
A critical connection between the thyroid and cricoid cartilages in the larynx.
Distal radioulnar joint
A pivotal joint that connects the distal ends of the radius and ulna, enabling forearm rotation.
Elbow joint
A complex joint facilitating the movement of the arm and the hand.
First carpometacarpal joint
A pivotal joint located at the base of the thumb, facilitating a wide range of thumb movements.
Glenohumeral joint
A highly mobile joint that connects the humerus to the scapula, allowing for a wide range of arm movements.
Hip joint
A crucial ball-and-socket joint that connects the lower limb to the pelvis, allowing for a wide range of movement.
Humeroradial joint
A pivotal joint that facilitates the movement of the forearm.
Humeroulnar joint
A pivotal joint that allows movement of the arm and elbow.
Incudomalleolar joint
A pivotal connection in the middle ear that facilitates sound transmission.
Incudostapedial joint
A unique joint that connects the incus and stapes, playing a pivotal role in the auditory system.
Interchondral joints
These are joints located between the costal cartilages of the ribs.
Interphalangeal joints of the foot
The joints connecting the bones of the toes, allowing for flexibility and movement.
Interphalangeal joints of the hand
The joints that connect the phalanges of the fingers, allowing for intricate movements.
Intervertebral joints
Critical components that provide flexibility and support to the spine.
Knee joint
A complex joint that facilitates movement of the lower limb while providing stability and support.
Lumbosacral joint
A critical junction that connects the lumbar spine to the sacrum, providing stability and mobility to the lower back.
Manubriosternal joint
A critical joint that connects the upper part of the sternum to the body of the sternum.
Metacarpophalangeal joints
These joints connect the bones of the hand to the fingers, allowing for a wide range of motion.
Metatarsophalangeal joints
The joints that connect the metatarsal bones of the foot to the proximal phalanges of the toes.
Proximal radioulnar joint
A pivotal joint in the forearm, facilitating the rotation of the radius around the ulna.
Pubic symphysis
A cartilage joint that connects the left and right pubic bones at the front of the pelvis.
Radioulnar joint
A critical connection that allows forearm rotation and movement of the wrist.
Sacrococcygeal joint
A critical joint facilitating movement at the base of the spine.
Sacroiliac joint
A crucial joint that connects the sacrum at the base of the spine with the iliac bones of the pelvis.
Shoulder joint
A highly mobile joint that connects the upper limb to the torso and allows for a wide range of motion.
Sternoclavicular joint
The vital joint connecting the upper limb to the torso.
Sternocostal joints
The joints that connect the sternum to the ribs, facilitating thoracic movement.
Subtalar joint
A vital joint located in the foot, playing a crucial role in movement and stability.
Sutures of the skull
The fibrous joints connecting the bones of the skull, allowing for slight movement and growth during development.
Synchondroses
A type of cartilaginous joint that allows for limited movement between bony structures.
Syndesmoses
A type of fibrous joint that connects bones through a band of dense connective tissue.
Talocrural joint
A pivotal joint that allows for mobility and stability in the ankle area.
Tarsometatarsal joints
The complex joints connecting the tarsal bones of the foot to the metatarsal bones.
Temporomandibular joint
A pivotal joint that connects the jawbone to the skull, allowing for essential movements such as chewing and speaking.
Tibiofibular joints
The joints that connect the tibia and fibula bones of the lower leg, allowing for stability and movement.
Wrist joint
This joint connects the forearm to the hand, allowing for a wide range of movements.
Xiphisternal joint
A vital structure in the human chest playing a significant role in rib articulation and thoracic stability.
Zygapophyseal joints
Joints that connect the vertebrae of the spine and allow for limited movement.
Ligaments and Tendons
Connective tissues that support and move joints by connecting bones to bones (ligaments) and muscles to bones (tendons).
Achilles tendon
A strong band of fibrous tissue connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Alar ligaments
The ligaments that connect the sides of the odontoid process of the second cervical vertebra to the sides of the foramen magnum.
Annular ligament
A fibrous band that stabilizes the radius bone in the forearm at the elbow joint.
Anterior cruciate ligament
A key ligament in the knee joint, crucial for stabilizing movement and preventing excessive motion.
Anterior longitudinal ligament
A strong band of connective tissue that helps stabilize the spine and maintain its alignment.
Anterior talofibular ligament
A crucial ligament that stabilizes the ankle joint and prevents excessive forward movement of the foot.
Arcuate popliteal ligament
A key structure in the posterior knee region, contributing to joint stability and motion.
Biceps tendon
A vital structure in the arm that connects the biceps muscle to the bones of the shoulder and elbow.
Calcaneofibular ligament
A critical structure in the ankle that contributes to stability and movement.
Collateral ligaments of the fingers
Important stabilizing structures that connect bone in the fingers, providing support during movement.
Coracoacromial ligament
A fibrous band that provides stability to the shoulder joint.
Coracoclavicular ligament
The ligament that connects the coracoid process of the scapula to the clavicle, providing stabilization to the shoulder.
Coronary ligaments of the knee
The connective tissue structures that stabilize the knee joint and anchor the menisci to the femur.
Deltoid ligament
A crucial ligament located in the inner ankle, providing stability and support to the joint.
Dorsal radiocarpal ligament
A key ligament that stabilizes the wrist joint during movements.
Extensor digitorum longus tendons
These tendons facilitate the extension of the toes and assist inFoot dorsiflexion.
Extensor expansion
A structure that facilitates the extension of the fingers and toes by connecting muscle tendons to the distal phalanges.
Extensor hallucis longus tendon
A tendon that plays a vital role in extending the big toe and aiding in foot movements.
Extensor tendons
Structures that connect muscles to bones, facilitating movement in the fingers and toes.
Flexor digitorum longus tendons
Tendons that play a crucial role in the movement of the toes and support foot flexion.
Flexor hallucis longus tendon
A vital tendon that connects muscles to the big toe, enabling movement and stability.
Flexor tendons
Tendons that facilitate the bending of joints, primarily in the fingers and toes.
Glenohumeral ligaments
A group of ligaments that play a critical role in stabilizing the shoulder joint.
Hamstring tendons
A group of tendons located at the back of the thigh, connecting important muscles to the bones.
Iliofemoral ligament
A key ligament that stabilizes the hip joint and plays a pivotal role in maintaining posture and movement.
Iliotibial band
A thick band of connective tissue that runs along the outer thigh and plays a key role in stabilizing the knee.
Inguinal ligament
A fibrous band that runs from the pubic bone to the iliac crest, providing structural support in the lower abdomen.
Interosseous membrane
A fibrous sheet that connects two bones and provides support and stability.
Interspinous ligaments
Tissues that stabilize adjacent vertebrae in the spine.
Intertransverse ligaments
Dense connective tissues that provide stability to the spine during movement and maintain alignment of the vertebrae.
Ischiofemoral ligament
A ligament providing stability to the hip joint and aiding in its range of motion.
Lateral collateral ligament
A critical structure in the knee, providing stability and support during movement.
Ligamentum arteriosum
A small, fibrous band that connects the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
Ligamentum flavum
A key structure that connects adjacent vertebrae and contributes to spinal stability.
Ligamentum nuchae
A fibrous structure that extends from the vertebrae in the neck to the back of the skull.
Ligamentum teres
This structure is a round ligament of the liver that plays a role in supporting the organ.
Long plantar ligament
This ligament plays a crucial role in maintaining the arch of the foot.
Medial collateral ligament
A crucial ligament that stabilizes the inner side of the knee joint.
Oblique popliteal ligament
A crucial structure that reinforces the posterior aspect of the knee joint.
Palmar radiocarpal ligament
A robust connective tissue structure that stabilizes the wrist joint and aids in its range of motion.
Palmaris longus tendon
A tendon crucial for wrist movement and grip strength.
Patellar ligament
This key structure connects the kneecap to the shinbone and plays a vital role in knee function.
Periodontal ligament
A connective tissue structure that supports and stabilizes teeth within their sockets.
Peroneal tendons
These tendons play a crucial role in the movement and stability of the foot and ankle.
Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
A key ligament that supports the medial aspect of the foot's arch.
Plantar fascia
A thick band of connective tissue that spans the bottom of the foot, supporting the arch and absorbing shock.
Plantaris tendon
A slender tendon that plays a key role in the motion of the lower leg and foot.
Posterior cruciate ligament
A critical ligament located within the knee joint that plays a vital role in stabilizing the knee.
Posterior longitudinal ligament
A crucial ligament that stabilizes the spine by running along the back of the vertebral bodies.
Posterior talofibular ligament
A key ligament that contributes to the stability of the ankle joint.
Pubofemoral ligament
A ligament that plays a crucial role in hip joint stability.
Quadriceps tendon
A robust structure that connects the quadriceps muscles to the kneecap, enabling movement and stability of the knee.
Radial collateral ligament
A crucial structure stabilizing the elbow joint, providing support during arm movements.
Rotator cuff tendons
A group of tendons that play a critical role in shoulder stability and movement.
Round ligament
A vital connective tissue structure that supports the uterus during pregnancy.
Sacrospinous ligament
A critical ligament that stabilizes the pelvis and connects the sacrum to the ischial spine.
Sacrotuberous ligament
A ligament connecting the sacrum to the ischial tuberosity of the pelvis.
Short plantar ligament
A fibrous connective tissue structure that supports the arch of the foot.
Supraspinous ligament
A strong band of fibrous connective tissue that runs along the spine, connecting the tips of the spinous processes.
Tibialis anterior tendon
A key structure that aids in dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot.
Tibialis posterior tendon
A crucial tendon that supports the arch of the foot and aids in balance and walking.
Transverse carpal ligament
A vital structure in the wrist that supports and stabilizes the carpal bones.
Transverse humeral ligament
A fibrous structure that helps stabilize the biceps tendon within the shoulder joint.
Transverse ligament of the atlas
A crucial ligament that stabilizes the first cervical vertebra, known as the atlas, in relation to the second cervical vertebra, called the axis.
Transverse ligament of the knee
A crucial ligament that maintains the stability and relationship between the lateral and medial menisci of the knee.
Triceps tendon
A crucial structure that connects muscle to bone, enabling arm movements.
Ulnar collateral ligament
Essential for stabilizing the inner aspect of the elbow joint during movement.